In a world increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, the value of data has never been higher. Whether it’s personal information, customer databases, or proprietary business secrets, data is now a prime target for cybercriminals—making data theft one of the most pressing cybersecurity threats of our time.
TL;DR
Data theft refers to the unauthorized access and extraction of data, typically with malicious intent. It can cause severe financial loss, reputational damage, and legal issues for individuals and businesses alike. To prevent data theft, it’s crucial to implement strong cybersecurity practices, educate users, and consistently update security measures. With a proactive approach, the risk can be significantly reduced.
What Is Data Theft?
Data theft is the act of stealing digital information such as personal identity details, financial records, intellectual property, or confidential business information. Unlike physical theft, data can be copied and distributed without the owner’s knowledge, often leaving minimal traces unless specifically monitored.
This form of cybercrime is not limited to identity thieves or lone hackers; it also includes sophisticated criminal organizations and sometimes even employees inside an organization acting with malicious intent. The primary goal behind data theft is usually profit—either by selling the information or exploiting it directly.
Common Types of Data Targeted
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Includes names, addresses, Social Security numbers, and other data that can be used to identify an individual.
- Financial Information: Credit card numbers, bank account details, and tax documents are prime targets for fraud and theft.
- Login Credentials: Usernames and passwords can be exploited to take control of online accounts or sell access on the dark web.
- Trade Secrets and Intellectual Property: Businesses are often targeted for proprietary information, such as formulas, algorithms, or marketing strategies.
- Customer Databases: Information about clients—including contact information and purchase history—is valuable on secondary markets.
How Data Theft Happens
Cybercriminals employ numerous methods to steal data, often exploiting both technological vulnerabilities and human errors. Some of the most prevalent techniques include:
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails or messages trick users into providing sensitive information.
- Malware and Ransomware: These malicious programs infiltrate systems to steal, encrypt, or destroy data.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Hackers intercept data being transmitted over unsecured networks.
- Brute Force Attacks: Automated tools attempt endless password combinations to gain unauthorized access.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors misuse their access rights to steal data for personal gain or sabotage.
- Physical Theft: Devices like laptops, USB drives, or smartphones are stolen and used to access data directly.
Consequences of Data Theft
The fallout from a data breach can be devastating, both financially and reputationally. Below are some of the consequences individuals and organizations might face:
- Financial Loss: From direct theft or through financial fraud stemming from stolen data.
- Legal Liability: Many countries have data protection laws. Violating these regulations can result in lawsuits or hefty fines.
- Reputational Damage: Loss of trust among customers and partners can take years to repair.
- Operational Disruption: Systems might need to be shut down or rebuilt post-breach, affecting productivity and revenue.
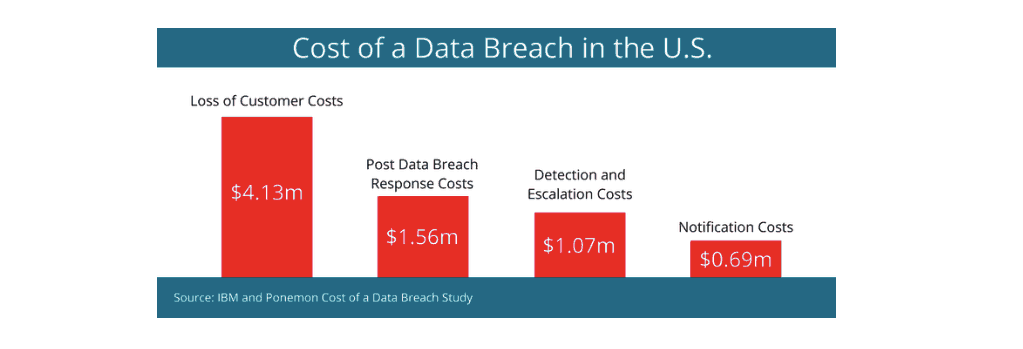
Real-world examples like the Equifax breach, Yahoo hacks, and more recently, the MOVEit data breach illustrate the potentially broad scope and high cost of data theft incidents.
How to Protect Against Data Theft
While it’s impossible to eliminate risk entirely, taking a multi-layered approach to security can drastically reduce the chances of data theft.
1. Strengthen Access Controls
- Use Strong Passwords: Encourage the use of complex, unique passwords and avoid reusing them across multiple sites.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an additional layer of verification beyond just a password.
- Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC): Restrict access to sensitive information based on user roles and responsibilities.
2. Regular Software Updates
Ensure all operating systems, software, and plugins are up-to-date with the latest security patches. Cybercriminals commonly exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated systems.
3. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the appropriate key. This applies to data in transit and at rest, including on mobile devices and external storage.
4. Secure Networks
- Use Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems: These can help monitor traffic and flag anomalous behavior.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi: Public networks are a common vector for MitM attacks. If necessary, use a VPN.
- Segment Your Network: Isolating sensitive areas of your network limits access and exposure in the event of a breach.
5. Employee Awareness and Training
Human error is one of the most common causes of security breaches. Regular training can educate employees on:
- Spotting phishing attempts
- Proper data handling and storage policies
- Using strong passwords and securing devices
6. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Always maintain secure backups of your data. In the event of ransomware or system failure, having reliable backups can be the difference between recovering quickly and permanent data loss.
7. Monitoring and Incident Response
- Continuous Monitoring: Use software tools to analyze network activity and detect suspicious behavior.
- Establish a Response Plan: Predefine roles, responsibilities, and procedures for responding to a breach.
What to Do If Your Data is Compromised
If you suspect you’ve fallen victim to data theft, acting quickly is essential to minimize damage:
- Disconnect Affected Devices: To stop the spread of malware or unauthorized access.
- Change Passwords Immediately: Especially for sensitive accounts like email, banking, or health portals.
- Notify Relevant Authorities: Report the breach to IT teams, management, or, in personal cases, your bank or law enforcement.
- Check for Unusual Activity: Monitor bank statements, credit scores, and login histories.
Conclusion
Data theft is a persistent and evolving threat in our increasingly digitized world. Whether you’re a business owner or an individual, protecting your personal and professional information must be a top priority. By understanding how data theft occurs and implementing layered defenses—both technical and behavioral—you can make it significantly harder for cybercriminals to succeed.
Ultimately, cybersecurity isn’t a one-time fix; it’s an ongoing process of vigilance, education, and adaptation. The cost of prevention is almost always less than the cost of recovery after a breach. Stay informed, stay secure.