Renaming a flash drive is a simple task that helps keep your files organized, especially when you use multiple USB devices. But sometimes, you might face an issue where the rename option doesn’t work either it’s greyed out, unresponsive, or the new name doesn’t save. This can be frustrating, especially if you’re trying to manage data across different devices.
In this guide, we’ll explain why you can’t rename your flash drive, what causes this issue, and how to fix it step-by-step on Windows, Mac, and Linux.
How to Rename a Flash Drive?
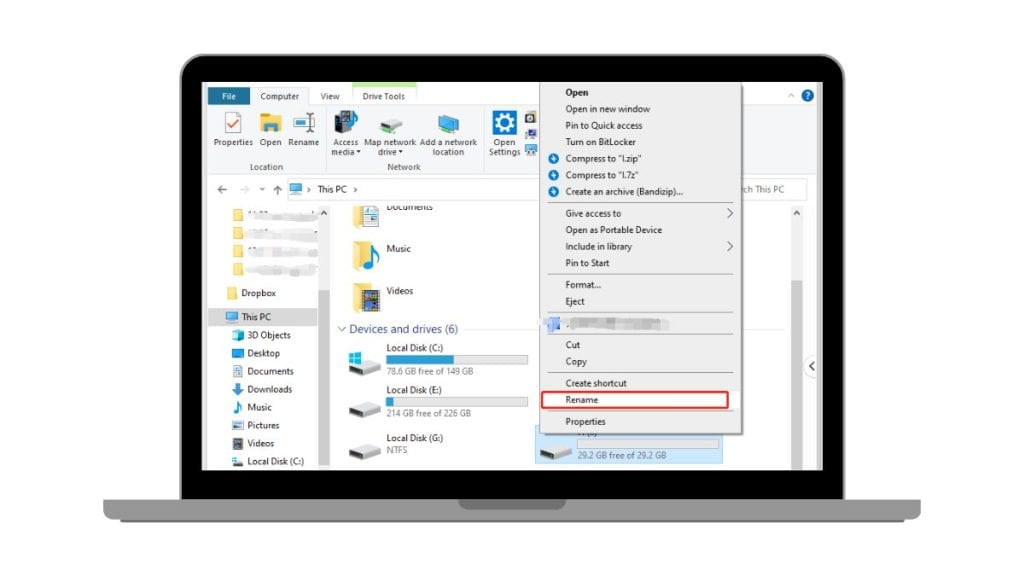
Before jumping into fixes, let’s cover the basics. Renaming a USB drive differs slightly depending on your operating system.
On Windows:
- Insert the flash drive.
- Open File Explorer.
- Right-click the USB drive and select Rename.
- Type the new name and press Enter.
On Mac:
- Connect the flash drive.
- Open Finder.
- Click the USB drive icon once.
- Press the Return (Enter) key.
- Type the new name and hit Return again.
On Linux:
- Plug in the flash drive.
- Open the file manager.
- Right-click the drive and choose Rename.
- Enter the new name and press Enter.
- For terminal users:
sudo mv /media/usb/oldname /media/usb/newname
- For terminal users:
If these steps don’t work, it’s time to find out why.
Common Issues When Renaming a Flash Drive

When renaming a flash drive doesn’t work, you might notice specific problems:
- Rename Option Greyed Out: The rename button is visible but disabled.
- Error Messages: Errors like “Access Denied”, “Drive is Write-Protected”, or “Cannot Rename”.
- Name Reverts After Renaming: The drive accepts the new name but reverts after you unplug it.
- Cannot Rename After Formatting: Even after formatting, the rename option fails.
What Causes Rename Flash Drive Not Working?
There are several reasons why you can’t rename your USB drive. Here are the most common causes:
- Write Protection Enabled: The drive is physically or digitally locked, preventing changes.
- File System Errors: Corruption in file systems like FAT32, NTFS, or exFAT.
- Permission Issues: Lack of administrative privileges, especially on shared or work computers.
- Virus or Malware: Malicious software can block access to USB functions.
- Corrupted Drive: Damaged sectors or bad blocks on the flash memory.
- Drive Letter Conflicts: When the USB shares the same drive letter with another device.
- Outdated USB Drivers: Old drivers can cause communication errors with the system.
- Software Conflicts: Apps running in the background (like antivirus software) may restrict USB operations.
How to Fix Rename Flash Drive Not Working
If your flash drive refuses to be renamed, try these solutions. Each step targets a specific issue.
Step 1: Check for Write Protection
Write protection can be hardware-based (with a switch) or software-based. Write protection blocks any changes, including renaming.
Here is how to check and fix it:
- Look for a small switch on the side of the flash drive. Toggle it to the unlocked position.
- On Windows, open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type: diskpart → list disk → select disk X (replace X with your USB number) → attributes disk clear readonly
- Press Enter after each command, then check if the rename option works.
Step 2: Run CHKDSK to Repair File System Errors
File system errors can prevent the system from saving changes to your flash drive. Corrupted sectors can stop rename operations from completing.
To fix it follow these steps:
- Open Command Prompt (Windows) as admin.
- Type:
chkdsk X: /f(replace X with your flash drive’s letter). - Press Enter and let the process finish.
- Safely eject and reinsert the drive, then try renaming it.
Step 3: Format the Flash Drive
If the file system is heavily damaged, formatting can reset it. Formatting removes corrupted data structures that block renaming.
Follow these steps to Format Safely:
- Backup your data first (formatting erases all files).
- Right-click the USB drive → Select Format.
- Choose FAT32 or exFAT (recommended for compatibility).
- Click Start, wait for the process to finish, and then rename the drive.
Step 4: Update USB Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can prevent proper communication between the flash drive and the operating system. Updated drivers ensure smooth operation of all USB functions.
Follow given steps to Update Drivers (Windows):
- Right-click the Start Menu → Select Device Manager.
- Expand Universal Serial Bus controllers.
- Right-click on your USB device → Click Update driver.
- Select Search automatically for drivers.
- Restart your computer and try renaming the drive again.
Step 5: Use Command Prompt (Advanced Method)
If GUI methods fail, using command-line tools can bypass system restrictions. Command Prompt can force the system to rename drives even when the interface is unresponsive.
How to Rename via Command Prompt (Windows):
- Open Command Prompt as admin.
- Type:
label X: NewName(replace X with your drive’s letter and NewName with the desired name). - Press Enter.
For Linux users:
- Open Terminal.
- Type:
sudo mv /media/usb/oldname /media/usb/newname - Press Enter and enter your password if prompted.
Are There Platform-Specific Issues?
Yes, rename issues can differ based on the operating system.
- Windows: Often caused by permission settings, outdated drivers, or registry issues.
- Mac: Issues with Spotlight indexing or file system permissions can prevent renaming.
- Linux: Terminal-based permission errors, especially with mounted drives.
- Cross-Platform Issues: Drives formatted in one OS may not allow renaming when used on another without proper permissions.
Practical Tips to Prevent Rename Issues
- Always Eject USB Drives Safely: This prevents data corruption.
- Scan Flash Drives Regularly: Use antivirus software to detect malware.
- Keep Drivers Updated: Regular updates reduce compatibility issues.
- Avoid Renaming During File Transfers: Make sure no files are being read or written.
- Limit Name Length: Keep the drive name under 11 characters for older systems.
- Use Compatible File Systems: exFAT works well across Windows, Mac, and Linux.
Conclusion
Renaming a flash drive is usually quick, but when it doesn’t work, it’s often due to write protection, file system errors, or permission issues. By following the steps in this guide, you can identify the cause and apply the right fix.
Have you faced this problem before? Did any of these solutions work for you?